BENEFIT
Advancing evidence-based medicine for better patient outcome
When the blood vessels of the heart, the coronary arteries, get obstructed this may cause a heart attack. Coronary artery disease affects more than 100 million people per year worldwide. For acute cases, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is at present the most effective procedure to reduce the mortality rate. A long, flexible thin plastic tube, a catheter, is inserted into an artery through a small incision in the groin or in the arm and navigated via the vessel tree to the location of the obstruction. Then a balloon at the tip of the catheter is inflated to re-open the vessel and a so-called stent is placed to keep the vessel open afterwards. In the USA alone, already around 2 million stents are placed in about 1 millionpatients every year. The decision to apply a stent used to be (and still largely is) based on visual assessment of the reduced diameter of the vessel due to the obstruction. However, clinical trials have shown that not all obstructions limit the flow of blood and that many stents are unnecessary. Furthermore, measuring of the pressure drop over the obstruction gives a more reliable indication than diameter reduction. The result is a significant reduction in the number of stent placements and thereby potential complications for the patient and costs for society.
Optimal diagnostic and treatment pathway for patients
The ITEA project BENEFIT aimed to support clinicians in selecting the optimal diagnostic and treatment pathway for patients. As a first, a procedure called QFR® (Quantitative Flow Ratio) analysis was developed by the Dutch SME Medis to calculate this pressure drop from the X-ray images which are acquired anyway. This saves the costs of a separate disposable catheter for pressure measurement - in the order of €500 to €1000 per patient - and promotes widespread adoption of pressure analysis to further reduce the overuse of stents. The company has gained CE and FDA approval and a large outcome study is running to make the procedure part of professional guidelines, including reimbursement by insurance companies.
Additionally, Leiden University Medical Center (LUMC) contributed to the imaging of coronary vessels and stents by Optical Coherence Tomography to check proper stent deployment and promote its worldwide standardisation. The algorithm may also indicate vulnerable regions in a coronary vessel, which will need additional treatment to reduce the risk of future cardiac events; this is currently being evaluated.
FEops HEARTguide gives our team increased confidence to perform TAVI in the most challenging of aortic valve anatomies.
These are two examples where the results of the BENEFIT project have improved medical imaging and the quantification of relevant parameters to support decision making and increase both clinical efficiency (overall costs of treatment and follow-up) and effectiveness (health for the patient). The continuously rising costs of healthcare worldwide make this a topic of prime importance for governments, insurance companies and healthcare providers. It fits in with the trend from ‘fee for service’ to ‘valuebased’ healthcare: payment for healthcare services will be based on the use of evidencebased professional guidelines and on the result for the patient, not on the number of procedures and the costs that the care provider has spent. BENEFIT focused on tools and protocols for imaging and treatment (image acquisition, image fusion, navigation tools) and quantified data before/during/after treatment, supported by common IT tools for structured collection and analysis of these data. This generic approach was applied to five different clinical use cases: diagnosis and treatment of cardiac blood vessels, cardiac valves, brain vessels, brain tumours and liver tumours.
The consortium consisted of 3 large industrial partners, 5 SMEs and 4 university hospitals to cover scientific input, input from clinical end users, technical innovation and market access. This has resulted in new products and dissemination in 70 publications, 3 master theses, 2 PhD theses, 2 book chapters, 60 presentations at scientific and commercial conferences and 7 patents.
Significant impact on business and society
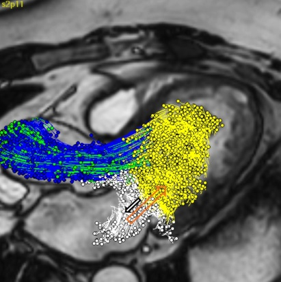
In the clinical use case of cardiac valves, the LUMC evaluated novel 4D flow Magnetic Resonance (MR) imaging protocols and image analysis methods for patient risk assessment. This research has resulted in various scientific papers, increased knowledge on the optimal usage of non-invasive MR imaging techniques and has contributed to the commercial release of a new 4D Flow MRI module for the Medis Suite MR image processing software.
The BENEFIT project also had a significant impact on FEops in terms of technology, funding and staffing. This Belgian SME received CE approval for its TAVIguide product which helps to improve placement of artificial heart valves by pre-operative imaging and simulation. It also recently secured an investment injection of €6 m to help drive commercial adoption of the FEops HEARTguideTM in the fast-growing market for transcatheter valve therapies. FEops has almost quadrupled its number of staff from 4 to 15 people.
For brain vessels, Philips has introduced a new commercial tool to the market for the treatment of cranial aneurysms, based on the research efforts performed within the scope of the BENEFIT programme. An aneurysm is a weak spot in the wall of a blood vessel which gets dilated due to the blood pressure and is at risk of rupturing. It is the first interventional tool to visualise and quantify flow patterns in a vessel and an aneurysm. It predicts the chance of long-term treatment success while the patient is still on the table and the catheter is in place. This means that the surgeon can take immediate additional actions in the event that the chance of success is too low, so that the risk for the patient is reduced as well as the need for repeated treatment. At the end of 2019 more than 250 units had been sold.
Also Erasmus MC, University Medical Center Rotterdam, contributed to stroke treatment by introducing novel tools and charts to increase the information from conventional CT and X-ray images. These tools and knowledge will be used in a subsequent large Dutch project, called CONTRAST (COllaboration for New TReatments of Acute STroke), where Erasmus MC will work with partners on imaging biomarkers for stroke and stroke treatment.
For brain tumour radiotherapy, Elekta received CE and FDA approval for its Leksell Gamma Knife ICON system with Cone beam CT (CBCT) for optimal patient positioning, in part due to BENEFIT. The CBCT positioning system allows frame and frameless workflow in radiotherapy such that patients do not need to carry the stereotactic frame for imaging before treatment planning. Thus it allows more flexibility and efficiency in treatment planning for both clinicians and patients. 107 Systems have been installed and clinically in use as of September 2019. There is also potential in upgrading the existing systems, i.e. over 200 worldwide. The automatic dose planning system that has also been developed and is currently being evaluated by clinical experts, with a partial contribution from BENEFIT, reduces planning time for test cases significantly by an estimated factor of 2 or more, while the inverse planner maintains performance.

In this same use case, Linköping University (LiU) in Sweden has published in BENEFIT a total of 10 journal papers, 3 conference papers and 2 book chapters, including on a new framework for MR diffusion imaging of brain tumours. For functional MRI, the most important publication, published in PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences) in 2016, showed severe problems with statistical methods used to analyse fMRI data. The paper has been covered by Science, The Economist, The New York Times, has been downloaded over 200,000 times and received over 1800 citations. LiU has continued the work in BENEFIT in collaboration with Harvard Medical School (USA) and Lund University (Sweden), for example through an SSF (Swedish foundation of strategic research) funded project about diffusion MRI.
The Dutch SME Quantib gained CE and FDA approval for its brain tumour analysis software and recently secured €4.5 m in fresh funding to support the company in its international expansion ambitions. Improvements developed within this project will continue to flow into future versions of the Quantib™ Brain and Quantib™ ND products. Furthermore, Quantib set up a framework to develop and evaluate deep-learning methods to quickly create prototypes and assess the clinical relevance. Prototypes include automated hip joint degeneration assessment based on X-rays to decrease hip joint replacements, and estimation of body fat percentage based on MRI e.g. to obtain better dose estimation for chemotherapy treatment. The prototypes are currently being evaluated in a clinical setting. From the start of BENEFIT until the present, Quantib grew from 6 employees to nearly 30, developed 4 products including certification, has installations in over 20 countries and initiated partnerships with 3 top medical university centres in the Netherlands.
Collaborative and complementary work on liver tumour treatments
In addition, for the use case of liver tumours, partners collaborated on different treatment alternatives. One option is surgical resection supported by intra-operative images from an endoscope. For reliable differentiation of healthy tissue and tumours Barco has developed a colour calibration procedure for the whole chain of endoscopes and medical displays which can now be performed in less than 5 seconds.
Philips improved its navigation support for catheter-based treatment in which the feeding vessels of the tumours are blocked by injection of small beads. The automatic 3D detection of tumour feeding vessels boosts detection accuracy by 26%, which means that fewer feeders are missed, resulting in at least 20% less recurrence than with 2D feeder detection, so better patient outcome and lower costs for follow-up treatment. Those beads may contain radioactive particles which will kill the tumour cells by their localised short-range radiation. To increase efficiency and accuracy of this procedure, UMC Utrecht has designed and evaluated algorithms for simultaneous X-ray fluoroscopic and nuclear imaging, for use in a hybrid interventional system. A prototype of such a system is currently in development boosted by subsequent Dutch and European grants.
Ablation is a method whereby tumours can be destroyed by heat from a needle tip. Erasmus MC has developed a method for the registration of pre-operative and intra-operative/post-operative CT images of the liver for use in ablation procedures at Erasmus MC to check whether indeed the whole tumour has been removed.
DEMCON has developed a CT guided needle positioning system (NPS). A first clinical study with the University Medical Center Groningen showed that ablation needles for the treatment of liver cancer with the NPS can be placed more accurately compared to freehand needle placement; freehand placement required on average one additional placement compared to placement by the NPS. More accurate needle positioning is expected to result in less damage of critical surrounding tissue and improved patient outcome for biopsies and ablation. Based on these positive results, improvements and extensions are currently being made to NPS technology, like compensation for patient movement, suitability for use in MRI and integration of ultrasound. However concrete market access plans are still under development.
Finally, UMC Utrecht developed methods for subject-specific four-dimensional liver motion modelling and motion correction of dynamic liver MR images, aimed at therapy selection and image-guided therapeutic procedures for patients with liver cancer. During the BENEFIT project, a collaboration on method development with Erasmus MC was set up, and useful contacts with companies as DEMCON and Quantib were established.
At the end of the project, integrated demonstrators of the collaborative and complementary work of the partners in all five use cases showed that BENEFIT has advanced evidence-based medicine by providing imaging tools, devices and a database for heterogeneous medical data. This closes the learning circle for continuous improvement of the efficiency and effectiveness of a broad array of minimally invasive surgery procedures. It also has prepared for a next step in healthcare, which is the adoption of artificial intelligence based on such quantified clinical data. This has been taken up by a new ITEA project called IMPACT.

